Christmas Island (The Andrews Sisters Song) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Christmas Island, officially the Territory of Christmas Island, is an Australian external territory comprising the island of the same name. It is located in the
World Statesmen
site and in Neale (1988), Bosman (1993), Hunt (2011), and Stokes (2012). The settlement of Silver City was built in the 1970s, with aluminium-clad houses that were supposed to be
 The island is about in greatest length and in breadth. The total land area is , with of coastline. The island is the flat summit of an underwater mountain more than high, which rises from about below the sea and only about above it.
The mountain was originally a
The island is about in greatest length and in breadth. The total land area is , with of coastline. The island is the flat summit of an underwater mountain more than high, which rises from about below the sea and only about above it.
The mountain was originally a
 As of the
As of the
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by th ...
, around south of Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's List ...
and Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
and around northwest of the closest point on the Australian mainland. It lies northwest of Perth
Perth is the capital and largest city of the Australian state of Western Australia. It is the fourth most populous city in Australia and Oceania, with a population of 2.1 million (80% of the state) living in Greater Perth in 2020. Perth is ...
and south of Singapore. It has an area of .
Christmas Island had a population of 1,692 residents , the majority living in settlements on the northern edge of the island. The main settlement is Flying Fish Cove
Flying Fish Cove ( zh, 飛魚灣, ms, Pantai Ikan Terbang) is the capital city and main settlement of Australia's Christmas Island. Although it was originally named after British survey-ship '' Flying-Fish'', many maps simply label it "The Set ...
. Historically, Asian Australians
Asian Australians refers to Australians of Asian ancestry, whether full or partial, including naturalised Australians who are immigrants from specific regions in Asia and descendants of such immigrants. At the 2021 census, the number of ances ...
of Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
, Malay
Malay may refer to:
Languages
* Malay language or Bahasa Melayu, a major Austronesian language spoken in Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei and Singapore
** History of the Malay language, the Malay language from the 4th to the 14th century
** Indonesi ...
, and Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
descent formed the majority of the population. Today, around two-thirds of the island's population is estimated to have Straits Chinese
The Peranakans () are an ethnic group defined by their genealogical descent from the first waves of Southern Chinese settlers to maritime Southeast Asia, known as Nanyang (), namely the British Colonial ruled ports in the Malay Peninsula, th ...
origin (though just 22.2% of the population declared a Chinese ancestry in 2021), with significant numbers of Malays and European Australian
European Australians are citizens or residents of Australia whose ancestry originates from the peoples of Europe. They form the largest panethnic group in the country. At the 2021 census, the number of ancestry responses categorised within Eu ...
s and smaller numbers of Straits Indians and Eurasians. Several languages are in use, including English, Malay
Malay may refer to:
Languages
* Malay language or Bahasa Melayu, a major Austronesian language spoken in Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei and Singapore
** History of the Malay language, the Malay language from the 4th to the 14th century
** Indonesi ...
, and various Chinese dialects. Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
and Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
are major religions on the island. The religion question in the Australian census
The Census in Australia, officially the Census of Population and Housing, is the national census in Australia that occurs every five years. The census collects key demographic, social and economic data from all people in Australia on census nig ...
is optional and 28% of the population do not declare their religious belief, if any.
The first European to sight Christmas Island was Richard Rowe of the ''Thomas'' in 1615. Captain William Mynors
William Mynors was an English sea-captain, master of the East India Company (EIC) vessel ''Royal Mary''. His voyage in 1643 discovered Christmas Island
Christmas Island, officially the Territory of Christmas Island, is an Australian exter ...
named it on Christmas Day (25 December) 1643. It was first settled in the late 19th century. Christmas Island's geographic isolation and history of minimal human disturbance has led to a high level of endemism
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsew ...
among its flora and fauna, which is of interest to scientists and naturalists. The majority (63 percent) of the island is included in the Christmas Island National Park
Christmas Island National Park is a national park occupying most of Christmas Island, an Australian territory in the Indian Ocean southwest of Indonesia. The park is home to many species of animal and plant life, including the eponymous Christma ...
, which features several areas of primary monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
al forest. Phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phospho ...
, deposited originally as guano
Guano (Spanish from qu, wanu) is the accumulated excrement of seabirds or bats. As a manure, guano is a highly effective fertilizer due to the high content of nitrogen, phosphate, and potassium, all key nutrients essential for plant growth. G ...
, has been mined on the island since 1899.
History
Geological history
Christmas Island is situated at the peak of abasalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
volcanic seamount which arose from the ocean floor in the Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene' ...
era about 60 million years ago, when the ocean eroded cliffs from uplifts, forming steep terraces and cliffs at the central plateau.
First visits by Europeans, 1643
The first European to sight the island was Richard Rowe of the ''Thomas'' in 1615. CaptainWilliam Mynors
William Mynors was an English sea-captain, master of the East India Company (EIC) vessel ''Royal Mary''. His voyage in 1643 discovered Christmas Island
Christmas Island, officially the Territory of Christmas Island, is an Australian exter ...
of the ''Royal Mary'', an English East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southe ...
vessel, named the island when he sailed past it on Christmas Day, in 1643. The island was included on English and Dutch navigation charts early in the 17th century, but it was not until 1666 that a map published by Dutch cartographer Pieter Goos
Pieter Goos (1616–1675) was a Dutch cartographer, copperplate engraver, publisher and bookseller. He was the son of Abraham Goos (1590–1643), also a cartographer and map seller. From 1666, Pieter Goos published a number of well produced ...
included the island. Goos labelled the island "Mony" or "Moni", the meaning of which is unclear.
English navigator William Dampier
William Dampier (baptised 5 September 1651; died March 1715) was an English explorer, pirate, privateer, navigator, and naturalist who became the first Englishman to explore parts of what is today Australia, and the first person to circumnav ...
, aboard the privateer Charles Swan's ship, ''Cygnet'', made the earliest recorded visit to the sea around the island in March 1688. He found it uninhabited. Dampier wrote an account of the visit. Dampier was trying to reach Cocos from New Holland. His ship was blown off course in an easterly direction, arriving at Christmas Island 28 days later. Dampier landed on the west coast, at "the Dales". Two of his crewmen became the first Europeans to set foot on Christmas Island.
Captain Daniel Beeckman of the ''Eagle'' passed the island on 5 April 1714, chronicled in his 1718 book, ''A Voyage to and from the Island of Borneo, in the East-Indies''.
Exploration and annexation
The first attempt at exploring the island was in 1857 by the crew of the ''Amethyst''. They tried to reach the summit of the island but found the cliffs impassable. During the 1872–1876 ''Challenger'' expedition to Indonesia, naturalist John Murray carried out extensive surveys. In 1886, CaptainJohn Maclear
John Fiot Lee Pearse Maclear (27 June 1838 in Cape Town – 17 July 1907 in Niagara) was an admiral in the Royal Navy, known for his leadership in hydrography.
He is best known for being commander of during the ''Challenger'' Expedition (1 ...
of , having discovered an anchorage in a bay that he named "Flying Fish Cove", landed a party and made a small collection of the flora
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous) native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms '' gut flora'' or '' skin flora''.
E ...
and fauna
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is ''flora'', and for fungi, it is '' funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as '' biota''. Zoo ...
. In the next year, Pelham Aldrich
Admiral Pelham Aldrich, CVO (8 December 1844 – 12 November 1930) was a Royal Navy officer and explorer, who became Admiral Superintendent of Portsmouth Docks.
Biography
He was born in Mildenhall, Suffolk, the son of Dr. Pelham Aldrich and El ...
, on board HMS ''Egeria'', visited the island for 10 days, accompanied by J. J. Lister, who gathered a larger biological and mineralogical collection.
Among the rocks then obtained and submitted to Murray for examination were many of nearly pure phosphate of lime
Calcium pyrophosphate (Ca2P2O7) is a chemical compound, an insoluble calcium salt containing the pyrophosphate anion. There are a number of forms reported: an anhydrous form, a dihydrate, Ca2P2O7·2H2O and a tetrahydrate, Ca2P2O7·4H2O. Deposition ...
. This discovery led to annexation
Annexation (Latin ''ad'', to, and ''nexus'', joining), in international law, is the forcible acquisition of one state's territory by another state, usually following military occupation of the territory. It is generally held to be an illegal act ...
of the island by the British Crown on 6 June 1888.
Settlement and exploitation
Soon afterwards, a small settlement was established in Flying Fish Cove by G. Clunies Ross, the owner of the Cocos (Keeling) Islands some to the southwest, to collect timber and supplies for the growing industry on Cocos. In 1897 the island was visited by Charles W. Andrews, who did extensive research on the natural history of the island, on behalf of theBritish Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It docum ...
.
Phosphate mining began in 1899 using indentured
An indenture is a legal contract that reflects or covers a debt or purchase obligation. It specifically refers to two types of practices: in historical usage, an indentured servant status, and in modern usage, it is an instrument used for commercia ...
workers from Singapore, British Malaya
The term "British Malaya" (; ms, Tanah Melayu British) loosely describes a set of states on the Malay Peninsula and the island of Singapore that were brought under British hegemony or control between the late 18th and the mid-20th century. U ...
, and China. John Davis Murray, a mechanical engineer and recent graduate of Purdue University
Purdue University is a public land-grant research university in West Lafayette, Indiana, and the flagship campus of the Purdue University system. The university was founded in 1869 after Lafayette businessman John Purdue donated land and money ...
, was sent to supervise the operation on behalf of the Phosphate Mining and Shipping Company. Murray was known as the "King of Christmas Island" until 1910, when he married and settled in London.
The island was administered jointly by the British Phosphate commissioners and district officers from the United Kingdom Colonial Office
The Colonial Office was a government department of the Kingdom of Great Britain and later of the United Kingdom, first created to deal with the colonial affairs of British North America but required also to oversee the increasing number of col ...
through the Straits Settlements
The Straits Settlements were a group of British territories located in Southeast Asia. Headquartered in Singapore for more than a century, it was originally established in 1826 as part of the territories controlled by the British East India Comp ...
, and later the Crown Colony of Singapore
Singapore was a British colony for 144 years, apart from a period of occupation under the Japanese Empire from 1942 to 1945 during the Pacific War.
When the Empire of Japan surrendered to the Allies in 1945, at the end of World War II, Singa ...
. Hunt (2011) provides a detailed history of Chinese indentured labour on the island during those years. In 1922, scientists unsuccessfully attempted to view a solar eclipse in late September from the island to test Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein ( ; ; 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory ...
's theory of relativity
The theory of relativity usually encompasses two interrelated theories by Albert Einstein: special relativity and general relativity, proposed and published in 1905 and 1915, respectively. Special relativity applies to all physical phenomena in ...
.
Japanese invasion
From the outbreak of the South-East Asian theatre ofWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
in December 1941, Christmas Island was a target for Japanese occupation because of its rich phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phospho ...
deposits. A naval gun was installed under a British officer and four NCOs and 27 Indian soldiers. The first attack was carried out on 20 January 1942, by , which torpedoed a Norwegian freighter, the ''Eidsvold''. The vessel drifted and eventually sank off West White Beach. Most of the European and Asian staff and their families were evacuated to Perth.
In late February and early March 1942, there were two aerial bombing raids. Shelling from a Japanese naval group on 7 March led the District Officer to hoist the white flag. But after the Japanese naval group sailed away, the British officer raised the Union Flag
The Union Jack, or Union Flag, is the ''de facto'' national flag of the United Kingdom. Although no law has been passed making the Union Flag the official national flag of the United Kingdom, it has effectively become such through precedent. ...
once more. During the night of 10–11 March, mutinous Indian troops, abetted by Sikh
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism, Sikhism (Sikhi), a Monotheism, monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Gu ...
policemen, killed Captain Leonard Williams and the four British NCOs in their quarters as they were sleeping. "Afterwards all Europeans on the island, including the district officer, who governed it, were lined up by the Indians and told they were going to be shot. But after a long discussion between the district officer and the leaders of the mutineers the executions were postponed and the Europeans were confined under armed guard in the district officer's house".
At dawn on 31 March 1942, a dozen Japanese bombers launched the attack, destroying the radio station. The same day, a Japanese fleet of nine vessels arrived, and the island was surrounded. About 850 men of the Japanese 21st and 24th Special Base Forces and 102nd Construction Unit came ashore at Flying Fish Cove
Flying Fish Cove ( zh, 飛魚灣, ms, Pantai Ikan Terbang) is the capital city and main settlement of Australia's Christmas Island. Although it was originally named after British survey-ship '' Flying-Fish'', many maps simply label it "The Set ...
and occupied the island. They rounded up the workforce, most of whom had fled to the jungle. Sabotaged equipment was repaired and preparations were made to resume the mining and export of phosphate. Only 20 men from the 21st Special Base Force were left as a garrison.
Isolated acts of sabotage and the torpedoing of the '' Nissei Maru'' at the wharf on 17 November 1942 meant that only small amounts of phosphate were exported to Japan during the occupation. In November 1943, over 60% of the island's population was evacuated to Surabaya
Surabaya ( jv, ꦱꦸꦫꦧꦪ or jv, ꦯꦹꦫꦨꦪ; ; ) is the capital city of the Provinces of Indonesia, Indonesian province of East Java and the List of Indonesian cities by population, second-largest city in Indonesia, after Jakarta. L ...
prison camps, leaving a total population of just under 500 Chinese and Malays and 15 Japanese to survive as best they could. In October 1945, re-occupied Christmas Island.
After the war, seven mutineers were traced and prosecuted by the Military Court in Singapore. In 1947, five of them were sentenced to death
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty, is the state-sanctioned practice of deliberately killing a person as a punishment for an actual or supposed crime, usually following an authorized, rule-governed process to conclude that t ...
. However, following representations made by the newly independent government of India, their sentences were reduced to penal servitude for life
Life is a quality that distinguishes matter that has biological processes, such as signaling and self-sustaining processes, from that which does not, and is defined by the capacity for growth, reaction to stimuli, metabolism, energ ...
.
Transfer to Australia
At Australia's request, the United Kingdom transferred sovereignty to Australia, with a $20 million payment from the Australian government toSingapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, borde ...
as compensation for the loss of earnings from the phosphate revenue. The United Kingdom's Christmas Island Act was given royal assent on 14 May 1958, enabling Britain to transfer authority over Christmas Island from Singapore to Australia by an order-in-council. Australia's Christmas Island Act was passed in September 1958 and the island was officially placed under the authority of the Commonwealth of Australia on 1 October 1958.
Under Commonwealth Cabinet Decision 1573 of 9 September 1958, D. E. Nickels was appointed the first official representative of the new territory. In a media statement on 5 August 1960, the minister for territories
The Minister for Infrastructure, Transport, Regional Development and Local Government in the Government of Australia is a position currently held by following the swearing in of the full Albanese ministry on 1 June 2022.
The Minister for Regio ...
, Paul Hasluck
Sir Paul Meernaa Caedwalla Hasluck, (1 April 1905 – 9 January 1993) was an Australian statesman who served as the 17th Governor-General of Australia, in office from 1969 to 1974. Prior to that, he was a Liberal Party politician, holding min ...
, said, among other things, that, "His extensive knowledge of the Malay language and the customs of the Asian people ... has proved invaluable in the inauguration of Australian administration ... During his two years on the island he had faced unavoidable difficulties ... and constantly sought to advance the island's interests."
John William Stokes succeeded him and served from 1 October 1960, to 12 June 1966. On his departure, he was lauded by all sectors of the island community. In 1968, the official secretary was retitled an administrator and, since 1997, Christmas Island and the Cocos (Keeling) Islands
)
, anthem = "''Advance Australia Fair''"
, song_type =
, song =
, image_map = Australia on the globe (Cocos (Keeling) Islands special) (Southeast Asia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of the Cocos (Keeling) Islands
, map_caption = ...
together are called the Australian Indian Ocean Territories
The Australian Indian Ocean Territories is the name since 1995 of an administrative unit under the Australian Department of Infrastructure, Transport, Regional Development, Communications and the Arts, consisting of two island groups in the In ...
and share a single administrator resident on Christmas Island. Recollections of the island's history and lifestyle, and lists and timetables of the island's leaders and events since its settlement are at thWorld Statesmen
site and in Neale (1988), Bosman (1993), Hunt (2011), and Stokes (2012). The settlement of Silver City was built in the 1970s, with aluminium-clad houses that were supposed to be
cyclone
In meteorology, a cyclone () is a large air mass that rotates around a strong center of low atmospheric pressure, counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to an anti ...
-proof. The 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami
An earthquake and a tsunami, known as the Boxing Day Tsunami and, by the scientific community, the Sumatra–Andaman earthquake, occurred at 07:58:53 local time (UTC+7) on 26 December 2004, with an epicentre off the west coast of northern Suma ...
centred off the western shore of Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
in Indonesia, resulted in no reported casualties, but some swimmers were swept some out to sea for a time before being swept back in.
Refugee and immigration detention
From the late 1980s and early 1990s, boats carryingasylum seekers
An asylum seeker is a person who leaves their country of residence, enters another country and applies for asylum (i.e., international protection) in that other country. An asylum seeker is an immigrant who has been forcibly displaced and mi ...
, mainly departing from Indonesia, began landing on the island. In 2001, Christmas Island was the site of the ''Tampa'' controversy, in which the Australian government stopped a Norwegian ship, MV ''Tampa'', from disembarking 438 rescued asylum-seekers. The ensuing standoff and the associated political reactions in Australia were a major issue in the 2001 Australian federal election
The 2001 Australian federal election was held in Australia on 10 November 2001. All 150 seats in the House of Representatives and 40 seats in the 76-member Senate were up for election. The incumbent Liberal Party of Australia led by Prime Minis ...
.
The Howard government operated the "Pacific Solution
Pacific Solution is the name given to the Government of Australia policy of transporting asylum seekers to detention centres on island nations in the Pacific Ocean, rather than allowing them to land on the Australian mainland. Initially imple ...
" from 2001 to 2007, excising Christmas Island from Australia's migration zone so that asylum seekers on the island could not apply for refugee status
A refugee, conventionally speaking, is a displaced person who has crossed national borders and who cannot or is unwilling to return home due to well-founded fear of persecution.
. Asylum seekers were relocated from Christmas Island to Manus Island
Manus Island is part of Manus Province in northern Papua New Guinea and is the largest of the Admiralty Islands. It is the fifth-largest island in Papua New Guinea, with an area of , measuring around . Manus Island is covered in rugged jungles w ...
and Nauru
Nauru ( or ; na, Naoero), officially the Republic of Nauru ( na, Repubrikin Naoero) and formerly known as Pleasant Island, is an island country and microstate in Oceania, in the Central Pacific. Its nearest neighbour is Banaba Island in Ki ...
. In 2006, an immigration detention centre, containing approximately 800 beds, was constructed on the island for the Department of Immigration and Multicultural Affairs
The Department of Immigration and Border Protection (DIBP) was a department of the Government of Australia that was responsible for immigration, citizenship and border control (including visa issuance). It has now been subsumed into the Depart ...
. Originally estimated to cost million, the final cost was over $400 million. In 2007, the Rudd government
Rudd Government may refer to the following Australian governments:
* Rudd government (2007–10)
Rudd Government may refer to the following Australian governments:
* Rudd government (2007–10)
* Rudd government (2013)
{{Dab ...
* Rudd gov ...
decommissioned Manus Regional Processing Centre
The Manus Regional Processing Centre, or Manus Island Regional Processing Centre (MIRCP), was one of a number of offshore Australian immigration detention facilities. The centre was located on the PNG Navy Base Lombrum (previously a Royal Aus ...
and Nauru detention centre
The Nauru Regional Processing Centre is an offshore Australian immigration detention facility in use from 2001 to 2008, from 2012 to 2019, and from September 2021. It is located on the South Pacific island nation of Nauru and run by the Gover ...
; processing would then occur on Christmas Island itself.
In December 2010, 48 asylum-seekers died just off the coast of the island in what became known as the Christmas Island boat disaster when their boat hit the rocks near Flying Fish Cove, and then smashed against nearby cliffs. In the case ''Plaintiff M61/2010E v Commonwealth of Australia'', the High Court of Australia
The High Court of Australia is Australia's apex court. It exercises Original jurisdiction, original and appellate jurisdiction on matters specified within Constitution of Australia, Australia's Constitution.
The High Court was established fol ...
ruled, in a 7–0 joint judgment, that asylum seekers detained on Christmas Island were entitled to the protections of the Migration Act. Accordingly, the Commonwealth was obliged to afford asylum seekers a minimum of procedural fairness when assessing their claims. , after the interception of four boats in six days, carrying 350 people, the Immigration Department stated that there were 2,960 "irregular maritime arrivals" being held in the island's five detention facilities, which exceeded not only the "regular operating capacity" of 1,094 people, but also the "contingency capacity" of 2,724.
The Christmas Island Immigration Reception and Processing Centre closed in September 2018. The Morrison government announced it would re-open the centre in February the following year, after Australia's parliament passed legislation giving sick asylum seekers easier access to mainland hospitals. In the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identif ...
, the government opened parts of the Immigration Reception and Processing Centre to be used as a quarantine facility to accommodate Australian citizens who had been in Wuhan
Wuhan (, ; ; ) is the capital of Hubei, Hubei Province in the China, People's Republic of China. It is the largest city in Hubei and the most populous city in Central China, with a population of over eleven million, the List of cities in China ...
, the point of origin of the pandemic. The evacuees arrived on 3 February. They left 14 days later to their homes on the mainland.
Geography
 The island is about in greatest length and in breadth. The total land area is , with of coastline. The island is the flat summit of an underwater mountain more than high, which rises from about below the sea and only about above it.
The mountain was originally a
The island is about in greatest length and in breadth. The total land area is , with of coastline. The island is the flat summit of an underwater mountain more than high, which rises from about below the sea and only about above it.
The mountain was originally a volcano
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are ...
, and some basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
is exposed in places such as The Dales and Dolly Beach, but most of the surface rock is limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
accumulated from coral
Corals are marine invertebrates within the class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact colonies of many identical individual polyps. Coral species include the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and sec ...
growth. The karst
Karst is a topography formed from the dissolution of soluble rocks such as limestone, dolomite, and gypsum. It is characterized by underground drainage systems with sinkholes and caves. It has also been documented for more weathering-resistant ro ...
terrain supports numerous anchialine caves. The summit of this mountain peak is formed by a succession of Tertiary
Tertiary ( ) is a widely used but obsolete term for the geologic period from 66 million to 2.6 million years ago.
The period began with the demise of the non-avian dinosaurs in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, at the start ...
limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
s ranging in age from the Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene' ...
or Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the ...
up to recent reef deposits, with intercalations of volcanic rock in the older beds.
Steep cliffs along much of the coast rise abruptly to a central plateau. Elevation ranges from sea level to at Murray Hill. The island is mainly tropical rainforest
Tropical rainforests are rainforests that occur in areas of tropical rainforest climate in which there is no dry season – all months have an average precipitation of at least 60 mm – and may also be referred to as ''lowland equatori ...
, 63% of which is national parkland. The narrow fringing reef
A reef is a ridge or shoal of rock, coral or similar relatively stable material, lying beneath the surface of a natural body of water. Many reefs result from natural, abiotic processes— deposition of sand, wave erosion planing down rock out ...
surrounding the island poses a maritime hazard.
Christmas Island lies northwest of Perth
Perth is the capital and largest city of the Australian state of Western Australia. It is the fourth most populous city in Australia and Oceania, with a population of 2.1 million (80% of the state) living in Greater Perth in 2020. Perth is ...
, Western Australia, south of Indonesia, ENE of the Cocos (Keeling) Islands
)
, anthem = "''Advance Australia Fair''"
, song_type =
, song =
, image_map = Australia on the globe (Cocos (Keeling) Islands special) (Southeast Asia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of the Cocos (Keeling) Islands
, map_caption = ...
, and west of Darwin, Northern Territory. Its closest point to the Australian mainland is from the town of Exmouth
Exmouth is a harbor, port town, civil parishes in England, civil parish and seaside resort, sited on the east bank of the mouth of the River Exe and southeast of Exeter.
In 2011 it had a population of 34,432, making Exmouth the List of town ...
, Western Australia.
Beaches
Christmas Island has of shoreline but only small parts of the shoreline are easily accessible. The island's perimeter is dominated by sharp cliff faces, making many of the island's beaches difficult to get to. Some of the easily accessible beaches include Flying Fish Cove (main beach), Lily Beach, Ethel Beach, and Isabel Beach, while the more difficult beaches to access include Greta Beach, Dolly Beach, Winifred Beach, Merrial Beach, and West White Beach, which all require a vehicle with four wheel drive and a difficult walk through dense rainforest.Climate
Christmas Island lies near the southern edge of the equatorial region. It has atropical monsoon climate
An area of tropical monsoon climate (occasionally known as a sub-equatorial, tropical wet climate or a tropical monsoon and trade-wind littoral climate) is a tropical climate sub-type that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification category ...
(Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (born 1951), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author and ...
''Am'') and temperatures vary little throughout the year. The highest temperature is usually around in March and April, while the lowest temperature is and occurs in August. There is a dry season from July to October with only occasional showers. The wet season is between November and June and includes monsoons
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
, with downpours of rain at random times of the day. Tropical cyclones
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depend ...
also occur in the wet season, bringing very strong winds, heavy rain, wave action, and storm surge
A storm surge, storm flood, tidal surge, or storm tide is a coastal flood or tsunami-like phenomenon of rising water commonly associated with low-pressure weather systems, such as cyclones. It is measured as the rise in water level above the n ...
.
Demographics
 As of the
As of the 2021 Australian census
The 2021 Australian census, simply called the 2021 Census, was the eighteenth national Census of Population and Housing in Australia. The 2021 Census took place on 10 August 2021, and was conducted by the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS). T ...
, the population of Christmas Island is 1,843. 22.2% of the population had Chinese ancestry (up from 18.3% in 2001), 17.0% had generic Australian ancestry (11.7% in 2001), 16.1% had Malay ancestry (9.3% in 2001), 12.5% had English ancestry (8.9% in 2001), and 3.8% of the population was of Indonesian origin. As of 2021, most are people born in Christmas Island and many are of Chinese and Malay origin. 40.8% of people were born in Australia. The next most common country of birth was Malaysia at 18.6%. 29.3% of the population spoke English as their family language, while 18.4% spoke Malay, 13.9% spoke Mandarin Chinese, 3.7% Cantonese and 2.1% Southern Min
Southern Min (), Minnan (Mandarin pronunciation: ) or Banlam (), is a group of linguistically similar and historically related Sinitic languages that form a branch of Min Chinese spoken in Fujian (especially the Minnan region), most of Taiwan ( ...
(Minnan). Additionally, there are small local populations of Malaysian Indians
Malaysian Indians or Indian Malaysians are Malaysian citizens of Indian or South Asian ancestry. Today, they form the third-largest group in Malaysia after the Malays and the Chinese. Most are descendants of those who migrated from India durin ...
and Eurasians.
The 2016 Australian census
The 2016 Australian census was the 17th national population census held in Australia. The census was officially conducted with effect on Tuesday, 9 August 2016. The total population of the Commonwealth of Australia was counted as – an incre ...
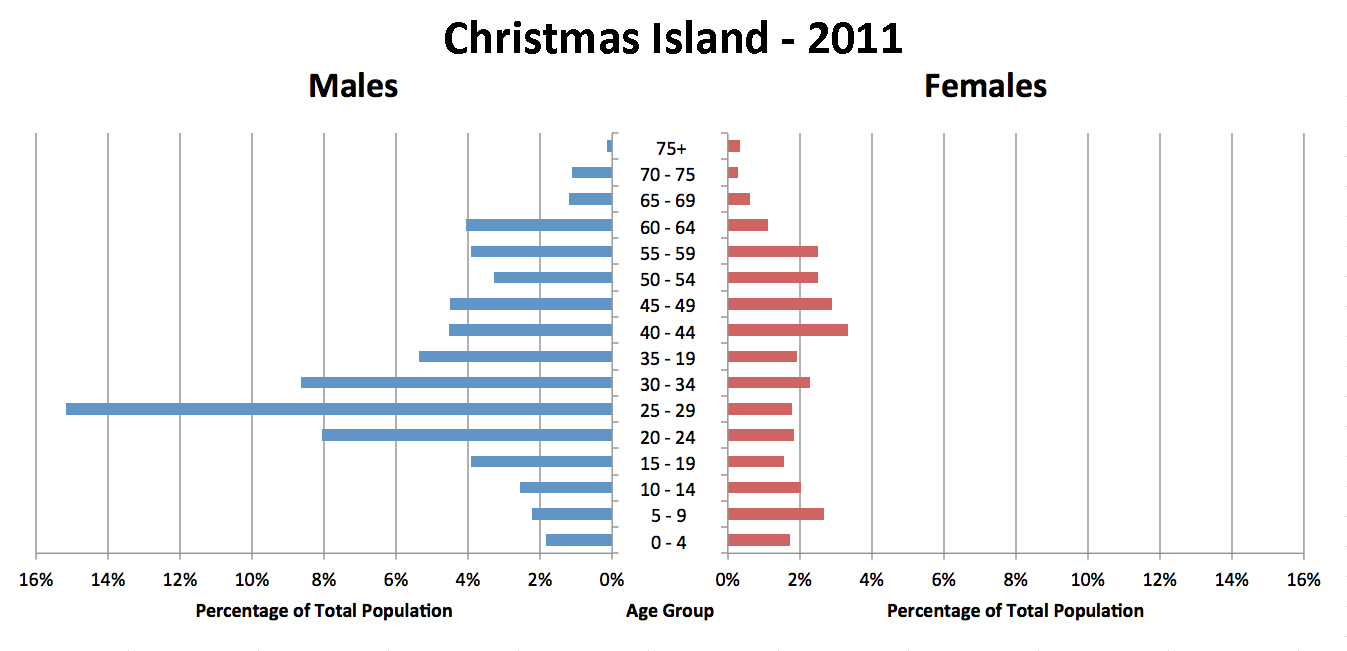
recorded that the population of Christmas Island was 40.5% female and 59.5% male, while in 2011 the figures had been 29.3% female and 70.7% male. In contrast, the 2021 figures for the whole of Australia were 50.7% female, 49.3% male. Since 1998 there has been no provision for childbirth on the island; expectant mothers travel to mainland Australia approximately one month before their expected date to give birth.
Government
Christmas Island is a non-self-governingexternal territory
A dependent territory, dependent area, or dependency (sometimes referred as an external territory) is a territory that does not possess full political independence or sovereignty as a sovereign state, yet remains politically outside the controlli ...
of Australia , part of the Australian Indian Ocean Territories
The Australian Indian Ocean Territories is the name since 1995 of an administrative unit under the Australian Department of Infrastructure, Transport, Regional Development, Communications and the Arts, consisting of two island groups in the In ...
administered by the Department of Infrastructure, Transport, Regional Development and Communications
The Department of Infrastructure, Transport, Regional Development and Communications and the Arts (DITRDCA), formerly Department of Infrastructure, Transport, Regional Development and Communications (DITRDC), is a department of the Australian ...
(from 29 November 2007 until 14 September 2010, administration was carried out by the Attorney-General's Department, and prior to this by the Department of Transport and Regional Services
The Department of Transport and Regional Services (DOTARS) was an Australian government department that existed between October 1998 and December 2007.
Scope
Information about the department's functions and/or government funding allocation coul ...
).
The legal system is under the authority of the Governor-General of Australia
The governor-general of Australia is the representative of the monarch, currently King Charles III, in Australia.administrator appointed by the Governor-General represents the
 Phosphate mining had been the only significant economic activity, but in December 1987 the Australian government closed the mine. In 1991, the mine was reopened by Phosphate Resources Limited, a consortium that included many of the former mine workers as shareholders and is the largest contributor to the Christmas Island economy.
With the support of the government, the $34 million Christmas Island Resort, Christmas Island Casino and Resort opened in 1993 but was closed in 1998. , the resort has re-opened without the casino.
The Australian government in 2001 agreed to support the creation of a commercial spaceport on the island; however, this has not yet been constructed and appears that it will not proceed. The Howard government built a temporary immigration detention centre on the island in 2001 and planned to replace it with a larger, modern facility at North West Point until Howard's defeat in the 2007 Australian federal election, 2007 elections.
Phosphate mining had been the only significant economic activity, but in December 1987 the Australian government closed the mine. In 1991, the mine was reopened by Phosphate Resources Limited, a consortium that included many of the former mine workers as shareholders and is the largest contributor to the Christmas Island economy.
With the support of the government, the $34 million Christmas Island Resort, Christmas Island Casino and Resort opened in 1993 but was closed in 1998. , the resort has re-opened without the casino.
The Australian government in 2001 agreed to support the creation of a commercial spaceport on the island; however, this has not yet been constructed and appears that it will not proceed. The Howard government built a temporary immigration detention centre on the island in 2001 and planned to replace it with a larger, modern facility at North West Point until Howard's defeat in the 2007 Australian federal election, 2007 elections.
 In 2016, the population was estimated to be Unspecified 27.7%, Islam, Muslim 19.4%, Buddhism, Buddhist 18.3%, None 15.3%, Roman Catholic 8.8%, Anglican 3.6%, Uniting Church in Australia, Uniting Church 1.2%, Other Protestant 1.7%, Other Christian 3.3% and other religions 0.6%
Religious beliefs are diverse and include
In 2016, the population was estimated to be Unspecified 27.7%, Islam, Muslim 19.4%, Buddhism, Buddhist 18.3%, None 15.3%, Roman Catholic 8.8%, Anglican 3.6%, Uniting Church in Australia, Uniting Church 1.2%, Other Protestant 1.7%, Other Christian 3.3% and other religions 0.6%
Religious beliefs are diverse and include
 Christmas Island is well known for its biological diversity. There are many rare species of animals and plants on the island, making nature-walking a popular activity. Along with the diversity of species, many different types of caves exist, such as plateau caves, coastal caves, raised coastal caves and alcoves, sea caves, fissure caves, collapse caves, and basalt caves; most of these are near the sea and have been formed by the action of water. Altogether, there are approximately 30 caves on the island, with Lost Lake Cave, Daniel Roux Cave, and Full Frontal Cave being the most well-known. The many freshwater springs include Hosnies Spring Ramsar, which also has a mangrove stand.
The Dales is a rainforest in the western part of the island and consists of seven deep valleys, all of which were formed by spring streams. Hugh's Dale waterfall is part of this area and is a popular attraction. The annual breeding migration of the Christmas Island red crabs is a popular event.
Fishing is another common activity. There are many distinct species of fish in the oceans surrounding Christmas Island. Snorkelling and swimming in the ocean are two other activities that are extremely popular. Walking trails are also very popular, for there are many beautiful trails surrounded by extravagant
Christmas Island is well known for its biological diversity. There are many rare species of animals and plants on the island, making nature-walking a popular activity. Along with the diversity of species, many different types of caves exist, such as plateau caves, coastal caves, raised coastal caves and alcoves, sea caves, fissure caves, collapse caves, and basalt caves; most of these are near the sea and have been formed by the action of water. Altogether, there are approximately 30 caves on the island, with Lost Lake Cave, Daniel Roux Cave, and Full Frontal Cave being the most well-known. The many freshwater springs include Hosnies Spring Ramsar, which also has a mangrove stand.
The Dales is a rainforest in the western part of the island and consists of seven deep valleys, all of which were formed by spring streams. Hugh's Dale waterfall is part of this area and is a popular attraction. The annual breeding migration of the Christmas Island red crabs is a popular event.
Fishing is another common activity. There are many distinct species of fish in the oceans surrounding Christmas Island. Snorkelling and swimming in the ocean are two other activities that are extremely popular. Walking trails are also very popular, for there are many beautiful trails surrounded by extravagant



 Christmas Island was uninhabited until the late 19th century, allowing many species to evolve without human interference. Two-thirds of the island has been declared a National Park, which is managed by the Australian Department of Environment and Heritage through Parks Australia. Christmas Island contains unique species, both of flora and fauna, some of which are threatened with, or have become, Extinct species, extinct.
Christmas Island was uninhabited until the late 19th century, allowing many species to evolve without human interference. Two-thirds of the island has been declared a National Park, which is managed by the Australian Department of Environment and Heritage through Parks Australia. Christmas Island contains unique species, both of flora and fauna, some of which are threatened with, or have become, Extinct species, extinct.
 A postal agency was opened on the island in 1901 and sold Postage stamps and postal history of the Straits Settlements, stamps of the Strait Settlements.
After the Japanese occupation (1942–1945), postage stamps of the British Military Administration (Malaya), British Military Administration in British Malaya, Malaya were in use, then stamps of Singapore.
In 1958, the island received its own postage stamps after being put under Australian custody. It had a large philatelic and postal independence, managed first by the Phosphate Commission (1958–1969) and then by the island's administration (1969–1993). This ended on 2 March 1993 when Australia Post became the island's postal operator; Christmas Island stamps may be used in Australia and Australian stamps may be used on the island.
A postal agency was opened on the island in 1901 and sold Postage stamps and postal history of the Straits Settlements, stamps of the Strait Settlements.
After the Japanese occupation (1942–1945), postage stamps of the British Military Administration (Malaya), British Military Administration in British Malaya, Malaya were in use, then stamps of Singapore.
In 1958, the island received its own postage stamps after being put under Australian custody. It had a large philatelic and postal independence, managed first by the Phosphate Commission (1958–1969) and then by the island's administration (1969–1993). This ended on 2 March 1993 when Australia Post became the island's postal operator; Christmas Island stamps may be used in Australia and Australian stamps may be used on the island.
monarch
A monarch is a head of stateWebster's II New College DictionarMonarch Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. Life tenure, for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority ...
and Australia and lives on the island. The territory falls under no formal state jurisdiction, but the Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to th ...
n Government provides many services as established by the Christmas Island Act.
The Australian government provides services through the Christmas Island Administration and the Department of Infrastructure and Regional Development. Under the federal government's Christmas Island Act 1958
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating the birth of Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25 as a religious and cultural celebration among billions of people around the world. A feast central to the Christian liturgical year ...
, Western Australian laws are applied to Christmas Island; non-application or partial application of such laws is at the discretion of the federal government. The act also gives Western Australian courts judicial power over Christmas Island. Christmas Island remains constitutionally distinct from Western Australia, however; the power of the state to legislate for the territory is delegated by the federal government. The kind of services typically provided by a state government elsewhere in Australia are provided by departments of the Western Australian government, and by contractors, with the costs met by the federal government. A unicameral Shire of Christmas Island
The Shire of Christmas Island is a local government area of the Australian external territory of Christmas Island (; post code: 6798). The island is grouped with Western Australia but is administered by the Attorney-General's Department and an ...
with nine seats provides local government services and is elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms. Elections are held every two years, with four or five of the members standing for election.
Federal politics
Christmas Island residents who are Australian citizens vote in Australian federal elections. Christmas Island residents are represented in the House of Representatives by theDivision of Lingiari
The Division of Lingiari is an Australian electoral division in the Northern Territory that covers the entirety of the territory outside of the Division of Solomon, which covers Darwin and surrounding areas. The division also includes the Ch ...
in the Northern Territory
The Northern Territory (commonly abbreviated as NT; formally the Northern Territory of Australia) is an states and territories of Australia, Australian territory in the central and central northern regions of Australia. The Northern Territory ...
and in the Senate by Northern Territory senators. At the 2019 Australian federal election, 2019 federal election, the Australian Labor Party, Labor Party received majorities from Christmas Island electors in both the House of Representatives and the Senate.
women held two of the nine seats in the Christmas Island Shire Council. Its second President was Lillian Oh, from 1993 to 1995.
Residents' views
Residents find the system of administration frustrating, with the island run by bureaucrats in the federal government, but subject to the laws of Western Australia and enforced by federal police. There is a feeling of resignation that any progress on local issues is hampered by the confusing governance system. A number of islanders support self-governance, including shire president Gordon Thompson, who also believes that a lack of news media to cover local affairs had contributed to political apathy among residents.Flag
In early 1986, the Christmas Island Assembly held a design competition for an island flag; the winning design was adopted as the informal flag of the territory for over a decade, and in 2002 it was made the official flag of Christmas Island.Economy
Culture
Ethnicity
Historically, the majority of Christmas Islanders were those of Chinese, Malay and Indian origins, the initial permanent settlers. Today, the majority of residents are Malaysian Chinese, Chinese, with significant numbers of European Australians and Malaysian Malays, Malays as well as smaller Malaysian Indian, Indian and Eurasian (mixed ancestry), Eurasian communities too. Since the turn of the 21st century and right up to the present, Europeans have mainly confined themselves to the Settlement, where there is a small supermarket and several restaurants; the Malays live in the Flying Fish Cove, also known as Kampong; and the Chinese reside in Poon San (Cantonese Chinese, Cantonese for "in the middle of the hill").Language
The main languages spoken at home on Christmas Island, according to respondents, are English (28%), Mandarin (17%), Malay (17%), with smaller numbers of speakers of Cantonese (4%) and Hokkien (2%). 27% did not specify a language. If the survey results are representative, then approximately 38% speak English, 24% Mandarin, 23% Malay, and 5% Cantonese.Religion
 In 2016, the population was estimated to be Unspecified 27.7%, Islam, Muslim 19.4%, Buddhism, Buddhist 18.3%, None 15.3%, Roman Catholic 8.8%, Anglican 3.6%, Uniting Church in Australia, Uniting Church 1.2%, Other Protestant 1.7%, Other Christian 3.3% and other religions 0.6%
Religious beliefs are diverse and include
In 2016, the population was estimated to be Unspecified 27.7%, Islam, Muslim 19.4%, Buddhism, Buddhist 18.3%, None 15.3%, Roman Catholic 8.8%, Anglican 3.6%, Uniting Church in Australia, Uniting Church 1.2%, Other Protestant 1.7%, Other Christian 3.3% and other religions 0.6%
Religious beliefs are diverse and include Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
, Taoism, Christianity, Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
and Confucianism. There is a mosque, a Christian church, a Baháʼí Faith, Baháʼí centre and around twenty Chinese temples and shrines, which include seven Buddhist temples (like Guan Yin Monastery (观音寺) at Gaze Road), ten Taoist temples (like Soon Tian Kong (顺天宫) in South Point and Grants Well Guan Di Temple) and shrines dedicated to Na Tuk Kong or Datuk Keramat on the island. There are many religious festivals, such as Chinese New Year, Spring Festival, Chap goh meh, Qingming Festival, Zhong Yuan Festival, Hari Raya, Christmas and Easter.
Cuisine
Christmas Island cuisine can best be described as an eclectic combination of traditional Australian cuisine and Asian cuisineWomen's issues
The main local organisation that "promotes and supports" the "status and interests" of female Christmas Islanders is the Christmas Island Women's Association which was established in 1989 and is a member organisation of the Associated Country Women of the World.Attractions
 Christmas Island is well known for its biological diversity. There are many rare species of animals and plants on the island, making nature-walking a popular activity. Along with the diversity of species, many different types of caves exist, such as plateau caves, coastal caves, raised coastal caves and alcoves, sea caves, fissure caves, collapse caves, and basalt caves; most of these are near the sea and have been formed by the action of water. Altogether, there are approximately 30 caves on the island, with Lost Lake Cave, Daniel Roux Cave, and Full Frontal Cave being the most well-known. The many freshwater springs include Hosnies Spring Ramsar, which also has a mangrove stand.
The Dales is a rainforest in the western part of the island and consists of seven deep valleys, all of which were formed by spring streams. Hugh's Dale waterfall is part of this area and is a popular attraction. The annual breeding migration of the Christmas Island red crabs is a popular event.
Fishing is another common activity. There are many distinct species of fish in the oceans surrounding Christmas Island. Snorkelling and swimming in the ocean are two other activities that are extremely popular. Walking trails are also very popular, for there are many beautiful trails surrounded by extravagant
Christmas Island is well known for its biological diversity. There are many rare species of animals and plants on the island, making nature-walking a popular activity. Along with the diversity of species, many different types of caves exist, such as plateau caves, coastal caves, raised coastal caves and alcoves, sea caves, fissure caves, collapse caves, and basalt caves; most of these are near the sea and have been formed by the action of water. Altogether, there are approximately 30 caves on the island, with Lost Lake Cave, Daniel Roux Cave, and Full Frontal Cave being the most well-known. The many freshwater springs include Hosnies Spring Ramsar, which also has a mangrove stand.
The Dales is a rainforest in the western part of the island and consists of seven deep valleys, all of which were formed by spring streams. Hugh's Dale waterfall is part of this area and is a popular attraction. The annual breeding migration of the Christmas Island red crabs is a popular event.
Fishing is another common activity. There are many distinct species of fish in the oceans surrounding Christmas Island. Snorkelling and swimming in the ocean are two other activities that are extremely popular. Walking trails are also very popular, for there are many beautiful trails surrounded by extravagant flora
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous) native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms '' gut flora'' or '' skin flora''.
E ...
and fauna
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is ''flora'', and for fungi, it is '' funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as '' biota''. Zoo ...
. 63% of the island is covered by the Christmas Island National Park
Christmas Island National Park is a national park occupying most of Christmas Island, an Australian territory in the Indian Ocean southwest of Indonesia. The park is home to many species of animal and plant life, including the eponymous Christma ...
.
Marine Park
Reefs near the islands have healthycoral
Corals are marine invertebrates within the class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact colonies of many identical individual polyps. Coral species include the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and sec ...
and are home to several rare species of marine life. The region, along with the Cocos (Keeling) Islands reefs, have been described as "Australia's Galapagos Islands".
In the 2021 budget the Australian Government committed $A39.1M to create two new marine parks off Christmas Island and the Cocos (Keeling) Islands. The parks will cover up to of Australian waters. After months of consultation with local people, both parks were approved in March 2022, with a total coverage of . The park will help to protect spawning of bluefin tuna from illegal international fishers, but local people will be allowed to practise fishing sustainably inshore in order to source food.
Flora and fauna



 Christmas Island was uninhabited until the late 19th century, allowing many species to evolve without human interference. Two-thirds of the island has been declared a National Park, which is managed by the Australian Department of Environment and Heritage through Parks Australia. Christmas Island contains unique species, both of flora and fauna, some of which are threatened with, or have become, Extinct species, extinct.
Christmas Island was uninhabited until the late 19th century, allowing many species to evolve without human interference. Two-thirds of the island has been declared a National Park, which is managed by the Australian Department of Environment and Heritage through Parks Australia. Christmas Island contains unique species, both of flora and fauna, some of which are threatened with, or have become, Extinct species, extinct.
Flora
The dense rainforest has grown in the deep soils of the plateau and on the terraces. The forests are dominated by 25 tree species. Ferns, orchids and vines grow on the branches in the humid atmosphere beneath the canopy (biology), canopy. The 135 plant species include at least 18 that are found nowhere else. The rainforest is in great condition despite the mining activities over the last 100 years. Areas that have been damaged by mining are now a part of an ongoing rehabilitation project. The island is small and covers 135 square kilometres of land which 63% of that land has been declared National park. Christmas Island's endemism, endemic plants include the trees ''Arenga listeri'', ''Pandanus elatus'' and ''Dendrocnide peltata'' var. ''murrayana''; the shrubs ''Abutilon listeri'', ''Colubrina pedunculata'', ''Grewia insularis'' and ''Pandanus christmatensis''; the vines ''Hoya aldrichii'' and ''Zehneria alba''; the herbaceous plant, herbs ''Asystasia alba'', ''Dicliptera maclearii'' and ''Peperomia rossii''; the grass ''Ischaemum nativitatis''; the fern ''Asplenium listeri''; and the orchids ''Brachypeza archytas'', ''Flickingeria nativitatis'', ''Phreatia listeri'' and ''Zeuxine exilis''.Fauna
Two species of native rats, the Maclear's rat, Maclear's and bulldog rats, have become extinct since the island was settled, while the Javan rusa deer has been introduced. The endemic (ecology), endemic Christmas Island shrew has not been seen since the mid-1980s and may be already extinct, while the Christmas Island pipistrelle (a small bat) is presumed to be extinct. The fruit bat (flying fox) species ''Pteropus natalis'' is only found on Christmas Island; its epithet ''natalis'' is a reference to that name. The species is probably the last native mammal, and an important pollinator and rainforest seed-disperser; the population is also in decline and under increasing pressure from land clearing and introduced pest species. The flying fox's low rate of reproduction (one pup each year) and high infant mortality rate makes it especially vulnerable and the conservation status is as critically endangered. Flying foxes are an 'umbrella' species helping forests regenerate and other species survive in stressed environments. The land crabs and seabirds are the most noticeable fauna on the island. Christmas Island has been identified by BirdLife International as both an Endemic Bird Area and an Important Bird Area because it supports five endemic species and five subspecies as well as over one per cent of the world populations of five other seabirds. Twenty terrestrial and intertidal species of crab have been described here, of which thirteen are regarded as true land crabs, being dependent on the ocean only for larval development. Robber crabs, known elsewhere as coconut crabs, also exist in large numbers on the island. The annual Christmas Island red crab, red crab mass migration (around 100 million animals) to the sea to spawn has been called one of the wonders of the natural world. This takes place each year around November – after the start of the wet season and in synchronisation with the cycle of the moon. Once at the ocean, the mothers release the embryos where they can survive and grow until they are able to live on land. The island is a focal point for seabirds of various species. Eight species or subspecies of seabirds nest on it. The most numerous is the red-footed booby, which nests in colonies, using trees on many parts of the shore terrace. The widespread brown booby nests on the ground near the edge of the seacliff and inland cliffs. Abbott's booby (listed as endangered) nests on tall emergent trees of the western, northern and southern plateau rainforest, the only remaining nesting habitat for this bird in the world. Another endangered and endemic bird, the Christmas frigatebird, has nesting areas on the northeastern shore terraces. The more widespread great frigatebirds nest in semi-deciduous trees on the shore terrace, with the greatest concentrations being in the North West and South Point areas. The common noddy and two species of bosun or tropicbirds also nest on the island, including the Golden Bosun, golden bosun (''P. l. fulvus''), a subspecies of the white-tailed tropicbird that is endemic to the island. Of the ten native land birds and shorebirds, seven are endemic species or subspecies. This includes the Christmas thrush and the Christmas imperial pigeon. Some 86 migrant bird species have been recorded as visitors to the island. Six species of butterfly are known to occur on Christmas Island. These are the Christmas swallowtail (''Papilio memnon''), striped albatross (''Appias olferna''), Christmas emperor (''Polyura andrewsi''), king cerulean (''Jamides bochus''), lesser grass-blue (''Zizina otis''), and Papuan grass-yellow (''Eurema blanda''). Insect species include the yellow crazy ant (''Anoplolepis gracilipes''), introduced to the island and since subjected to attempts to destroy the supercolony, supercolonies that emerged with aerial spraying of the insecticide Fipronil.Media
Christmas Island has access to a range of modern communication services. Radio broadcasts from Australia include Radio National, ABC Radio National, ABC Kimberley, Triple J and Red FM (Australia), Red FM. All services are provided by satellite links from the mainland. Broadband internet became available to subscribers in urban areas in mid-2005 through the local internet service provider, Christmas Island Internet Administration, CIIA (formerly dotCX). Christmas Island, due to its close proximity to Australia's northern neighbours, falls within many of the satellite footprints throughout the region. This results in ideal conditions for receiving various Asian broadcasts, which locals sometimes prefer to those emanating from Western Australia. Additionally, ionospheric conditions are conducive to terrestrial radio transmissions, from High frequency, HF through Very high frequency, VHF and sometimes into Ultra high frequency, UHF. The island plays home to a small array of radio equipment that spans a good chunk of the usable spectrum. A variety of government-owned and operated antenna systems are employed on the island to take advantage of this.Television
Free-to-air digital television stations from Australia are broadcast in the same time zone as Perth, and are broadcast from three separate locations: Cable television from Australia, Malaysia, Singapore and the United States commenced in January 2013.Telecommunications
Telephone services are provided by Telstra and are a part of the Australian network with the same prefix as Western Australia, South Australia and the Northern Territory (08). A GSM mobile telephone system on the 900 MHz band replaced the old analogue network in February 2005.Newspapers
TheShire of Christmas Island
The Shire of Christmas Island is a local government area of the Australian external territory of Christmas Island (; post code: 6798). The island is grouped with Western Australia but is administered by the Attorney-General's Department and an ...
publishes a fortnightly newsletter, The Islander (Christmas Island), ''The Islander''. There are no independent newspapers.
Postage stamps
 A postal agency was opened on the island in 1901 and sold Postage stamps and postal history of the Straits Settlements, stamps of the Strait Settlements.
After the Japanese occupation (1942–1945), postage stamps of the British Military Administration (Malaya), British Military Administration in British Malaya, Malaya were in use, then stamps of Singapore.
In 1958, the island received its own postage stamps after being put under Australian custody. It had a large philatelic and postal independence, managed first by the Phosphate Commission (1958–1969) and then by the island's administration (1969–1993). This ended on 2 March 1993 when Australia Post became the island's postal operator; Christmas Island stamps may be used in Australia and Australian stamps may be used on the island.
A postal agency was opened on the island in 1901 and sold Postage stamps and postal history of the Straits Settlements, stamps of the Strait Settlements.
After the Japanese occupation (1942–1945), postage stamps of the British Military Administration (Malaya), British Military Administration in British Malaya, Malaya were in use, then stamps of Singapore.
In 1958, the island received its own postage stamps after being put under Australian custody. It had a large philatelic and postal independence, managed first by the Phosphate Commission (1958–1969) and then by the island's administration (1969–1993). This ended on 2 March 1993 when Australia Post became the island's postal operator; Christmas Island stamps may be used in Australia and Australian stamps may be used on the island.
Transport
A container port exists at Flying Fish Cove with an alternative container-unloading point to the east of the island at Norris Point, intended for use during the December-to-March "swell season" of rough seas. The standard gauge Christmas Island Phosphate Co.'s Railway from Flying Fish Cove to the phosphate mine was constructed in 1914. It was closed in December 1987, when the Australian government closed the mine, and since has been recovered as scrap, leaving only earthworks in places. Virgin Australia provides two weekly flights to Christmas Island Airport from Perth, Western Australia. Garuda Indonesia conducts weekly open-charter flights from/to Jakarta, with bookings done through Christmas Island Travel Exchange. Malindo Air operate fortnightly open-charter flights from/to Kuala Lumpur, with bookings done through Evercrown Air Services. Hire cars are available from the airport however no franchised companies are represented. CI Taxi Service also operates most days. Due to the lack of 3G or 4G, the island's sole taxi operator could not meet the requirement issued by WA Department of Transport to install electronic meters, and the operator was forced to close at the end of June 2019. The road network covers most of the island and is of generally good quality, although four-wheel drive vehicles are needed to reach some of the more distant parts of the rainforest or the more isolated beaches on the rough dirt roads.Education
The island-operated Day care, crèche is in the Recreation Centre. Christmas Island District High School, catering to students in grades K-12#P–12, P-12, is run by the Western Australian Education Department. There are no universities on Christmas Island. The island has one public library.Sport
Cricket and rugby league are the two main organised sports on the island. The Christmas Island Cricket Club was founded in 1959, and is now known as the Christmas Island Cricket and Sporting Club. In 2019 the club celebrated its 60-year anniversary. The club entered its first representative team into the WACA Country Week in 2020, where they were runners up in the F-division. Rugby league is growing in the island: the first game was played in 2016, and a local committee, with the support of NRL Western Australia, is willing to organise matches with nearby Cocos (Keeling) Islands, Cocos Islands and to create a rugby league competition in the Indian Ocean region.See also
* Outline of Christmas Island * Index of Christmas Island–related articles * .cx *Cocos (Keeling) Islands
)
, anthem = "''Advance Australia Fair''"
, song_type =
, song =
, image_map = Australia on the globe (Cocos (Keeling) Islands special) (Southeast Asia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of the Cocos (Keeling) Islands
, map_caption = ...
* Norfolk Island
Notes
References
* * *Further reading
* 96 pages, including many b&w photographs. * 197 pages including many photographs and plates. * * * * 263 pages including photographs. * 112 pages including many photographs. * * 60 pages including colour photographs. * 133 pages including many colour photographs. * 76 pages including colour photographs. * * * * 207 pages including many b&w photographs. * 288 pages pictorial illustration of crabs. * 238 pages. * * {{coord, 10, 29, 24, S, 105, 37, 39, E, region:CX_type:isle_dim:30000, display=title Christmas Island, Island countries of the Indian Ocean Islands of Australia Islands of Southeast Asia Important Bird Areas of Australian External Territories British rule in Singapore British Malaya in World War II, . English-speaking countries and territories Malay-speaking countries and territories States and territories of Australia States and territories established in 1957 1957 establishments in Australia Important Bird Areas of Indian Ocean islands Endemic Bird Areas